

Blockchain in Finance: Impacts, Use Cases & Future Trends






Financial platforms face growing pressure to modernize amid rising customer expectations, faster digital services, heightened fraud risks, regulatory demands, and competition from digital-first companies.
Legacy systems struggle with speed, transparency, and scalability, making modernization essential for trust, efficiency, and long-term growth today.
Blockchain adoption is on the rise in fintech and banking as institutions seek secure, transparent, and efficient systems. Financial firms use blockchain to improve payments, reduce fraud, shorten settlement times, and enhance trust.
The growing investments, pilots, and real-world deployments suggest strong confidence in blockchain-driven transformation.
This article explains blockchain basics, why financial platforms are adopting it, major use cases, benefits, risks, future trends, and how financial businesses can prepare for blockchain-driven modernization and long-term digital transformation.
Blockchain is a shared digital record where transactions are stored in blocks and linked together. Multiple participants verify each record before being added.
Once recorded, information cannot be easily changed, making blockchain a secure and reliable way to track transactions without a central authority.
Decentralized ledgers work by sharing the same transaction record across many computers. Each participant keeps an updated copy. When a transaction occurs, the network agrees on its validity before recording it.
This shared control reduces errors, manipulation, and reliance on a single controlling organization.
Traditional systems rely on central databases controlled by one organization, creating delays and single points of failure. Blockchain distributes records across many participants, improving transparency and trust.
Updates occur through shared agreement, reducing manual checks, reconciliation, and reliance on intermediaries for verification.
As we have seen in our earlier blog on how fintech is disrupting the banking sector, now with the rise of blockchain – a technology that has the potential to further disrupt the financial industry that we use every day for our business transactions. Let us see the impacts it may create in the financial sectors.
As for the traditional payment system where contracts are fulfilled when certain criteria are met and validated by the central authority. In blockchain transactions, the contracts are stored in public ledger surpassing the middlemen to complete the agreement between the two parties smartly in no time.
Blockchains technology has the potential to gear up the real-time payment mechanism that can provide cost-effective techniques for many financial intermediaries who still look upon to the central authority for clearing and settlement. Distributed ledger mechanism leads to inordinate delay in settling transactions and customer dissatisfaction which could be used as a driving force to address the new technology solutions which can better solve these problems.
Let us understand how the payment system works in blockchains. For instance, if A wants to send money to B, the transaction is made as a block and sends the information to the earlier participants who were connected with the same money for validating their transactions for approval. Once the deal is approved the money is transferred to B and gets recorded in the ledger sequentially.
There is no central authority for clearing the transactions. This is the most significant advantage in blockchain as the mechanism is decentralized.
Centralized payment systems are prone to risk as the attacker needs to concentrate on the single entry point. In distributed ledger, one needs to access all networks simultaneously that are connected to the particular transaction that is impossible to succeed. As such these records hold undisputable proof of identity and ownership that prevents fraud and counterfeiting. Blockchain works on a trusted platform where the parties that validate the transactions are called miners. As the data are interconnected transaction gets verified automatically.
Financial platforms are adopting blockchain to address trust gaps, slow processes, rising costs, and complex compliance needs. The technology offers a new foundation for secure, transparent, and efficient financial operations across diverse services.
Blockchain improves trust by providing a shared and visible transaction record for all participants. Every update is recorded permanently and can be traced.
This transparency reduces disputes, fraud, and hidden changes, helping financial platforms build greater confidence among customers, partners, and regulators alike.
Blockchain reduces processing time by removing manual checks and third-party verification steps. Transactions move directly between participants and are confirmed faster.
Lower dependence on intermediaries reduces fees, operational overhead, and delays, making financial services more efficient and affordable at scale.
Traditional settlement cycles can take days due to multiple approvals and reconciliations. Blockchain enables near real-time settlement by updating records instantly across participants.
Faster settlement improves cash flow, reduces counterparty risk, and allows financial platforms to operate with greater certainty and liquidity.
Blockchain supports compliance by maintaining clear, time-stamped transaction histories that cannot be altered. Regulators can audit records more easily without manual reporting.
Automated rules ensure consistent policy enforcement, helping financial platforms meet regulatory requirements while significantly reducing compliance costs and operational complexity.
Blockchain delivers meaningful benefits to financial platforms by improving security, efficiency, transparency, and cost control.
These advantages help organizations modernize operations while building trust and resilience in increasingly digital financial environments.
Blockchain enhances transaction security through shared verification and permanent records. Once confirmed, transactions cannot be altered easily.
This reduces fraud, data manipulation, and unauthorized changes, helping financial platforms protect sensitive information and maintain strong customer and partner confidence.
By enabling direct transactions between participants, blockchain reduces reliance on intermediaries. Fewer middle layers mean simpler processes, faster execution, and lower fees.
Financial platforms benefit from streamlined operations and greater control over transaction flows and service delivery models.
Blockchain processes transactions quickly by removing manual reconciliation and approval steps. Shared records update instantly across participants.
Faster processing improves customer satisfaction, supports real-time services, and allows financial platforms to handle higher transaction volumes without proportional increases in operational effort.
Automation and reduced intermediaries help lower operational costs. Blockchain minimizes paperwork, manual reviews, and reconciliation activities.
Financial platforms reduce administrative expenses while improving accuracy, enabling them to scale services efficiently without significantly increasing staffing or infrastructure costs.
Blockchain provides a clear and shared view of transactions for all authorized participants. This transparency reduces disputes and increases accountability.
Financial platforms can demonstrate integrity, simplify audits, and strengthen trust among customers, partners, and regulators by maintaining consistent, visible transaction records.
Blockchain is being applied across financial services to improve security, efficiency, and trust.
Its flexibility supports payments, lending, fraud prevention, and digital assets, enabling platforms to redesign traditional financial processes with modern digital foundations.
Blockchain enables faster and more secure banking payments by reducing intermediaries and processing steps. Transactions settle quickly with shared verification.
This improves customer experience, lowers fees, and supports round-the-clock payments, especially for digital banks and modern financial platforms serving global users.
Smart contracts automatically execute agreements when conditions are met. In lending, they can release funds, calculate interest, and enforce repayments without manual intervention.
This automation reduces errors, speeds up approvals, and increases trust between lenders and borrowers through transparent, predictable rules.
Blockchain strengthens fraud detection by creating tamper-resistant identity records. User identities can be verified once and reused securely. Transaction histories help detect unusual patterns early.
This reduces identity theft, account misuse, and unauthorized access while improving onboarding speed and user trust.
Cross-border payments often involve delays, high fees, and multiple intermediaries. Blockchain simplifies this by enabling direct transfers with shared verification. Funds move faster and at a lower cost.
This benefits businesses and individuals sending money internationally with greater transparency and reliability.
Decentralized finance platforms use blockchain to offer financial services without traditional intermediaries. Users can lend, borrow, trade, or earn returns directly through transparent systems.
These platforms expand access to financial services while giving users greater control over their assets and greater visibility into transactions.
Asset tokenization converts physical or financial assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. This allows easier trading, fractional ownership, and improved liquidity.
Financial platforms use tokenization to modernize asset management, reduce paperwork, and broaden investment opportunities.
Blockchains can be used in different scenarios in the business that deals with value, asset, agreements, record keeping or data storage, contracts and cryptocurrencies.
Blockchain startup Symbiont, a company based in New York is using blockchain technology to develop smart contracts to be used in the trading platform. As discussed earlier how blockchains can transform trading sector (link it to the Blockchain in Trading Arena if possible), Symbiont helps in converting complex financial instruments to understandable language onto a distributed ledger.
From crop to cup, Bext360 uses blockchain technology built by Stellar to assert and assign codes to quality coffee cherries. The machine assorting the cherries assigns tokens to each quality and tracks the product across its lifespan. Coffee supply chains are greatly benefitted by blockchain technology that is built to suit their business.
By 2027, 10 percent of global gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to be stored on blockchain technology. Currently, the total worth of bitcoin in the blockchain is around $20 billion, or about 0.025% of global GDP of around $80 trillion. And since there are only 21 million bitcoins that are going to be produced, their value is only going to keep increasing. Bitcoin had started in 2010 when it was valued at only $0.008, and now in 2017, 1 Bitcoin equals $7,415.86.
As we have seen in the past, with the revolution of the internet, Fintech innovations blossomed and we see the same trendsetter on the rise with the innovation of blockchain technology, all thanks to Satoshi Nakamoto the name often found on the internet credited with the creation of bitcoin.
Some of the wallets that are powered by blockchain technology are given below for your reference. To find out more details about the wallets pursue the link given on each wallet.
Xapo is a company based in Switzerland that provides a bitcoin wallet with a bitcoin-based debit card. It also provides access to the cold storage vault. Ledger is a Cryptocurrency hardware wallet that safeguards crypto assets for individuals and companies. Trezor is a Bitcoin hardware wallet to store and secure your bitcoins. It also provides a variety of alternative digital currencies with a single device.
Leaders who see blockchain technology as an opportunity and not as a threat will lead the business organization to competitive advantage, efficiency in carrying out the business and overcome security threats. Blockchain can well become the potential game changer in the financial industry.
Despite its advantages, blockchain adoption presents challenges related to regulation, scalability, integration, privacy, and sustainability.
Financial platforms must carefully evaluate these risks to ensure responsible and effective implementation aligned with business and regulatory expectations.
Blockchain regulations vary across regions and continue to evolve. Unclear rules can create compliance risks and slow adoption.
Financial platforms must monitor regulatory changes closely, engage with authorities, and design flexible systems that can adapt to new legal and reporting requirements.
Some blockchain networks struggle to handle high transaction volumes efficiently. Processing delays and higher costs may occur during peak usage.
Financial platforms must carefully assess performance needs and consider scalable designs or hybrid approaches to support growth without compromising the user experience.
Integrating blockchain with existing financial systems can be complex. Legacy infrastructure may not easily support new data models or processes.
Successful adoption requires careful planning, skilled teams, and gradual implementation to ensure continuity, data consistency, and minimal disruption to ongoing operations.
While blockchain offers transparency, storing sensitive financial data on shared ledgers raises privacy concerns.
Financial platforms must balance openness and confidentiality by using access controls and encryption to protect personal information while effectively meeting regulatory and customer privacy expectations.
Some blockchain networks consume significant energy due to their validation processes. This raises sustainability concerns for financial platforms focused on environmental responsibility.
Choosing energy-efficient technologies and exploring alternative validation methods can help reduce environmental impact and support long-term adoption.
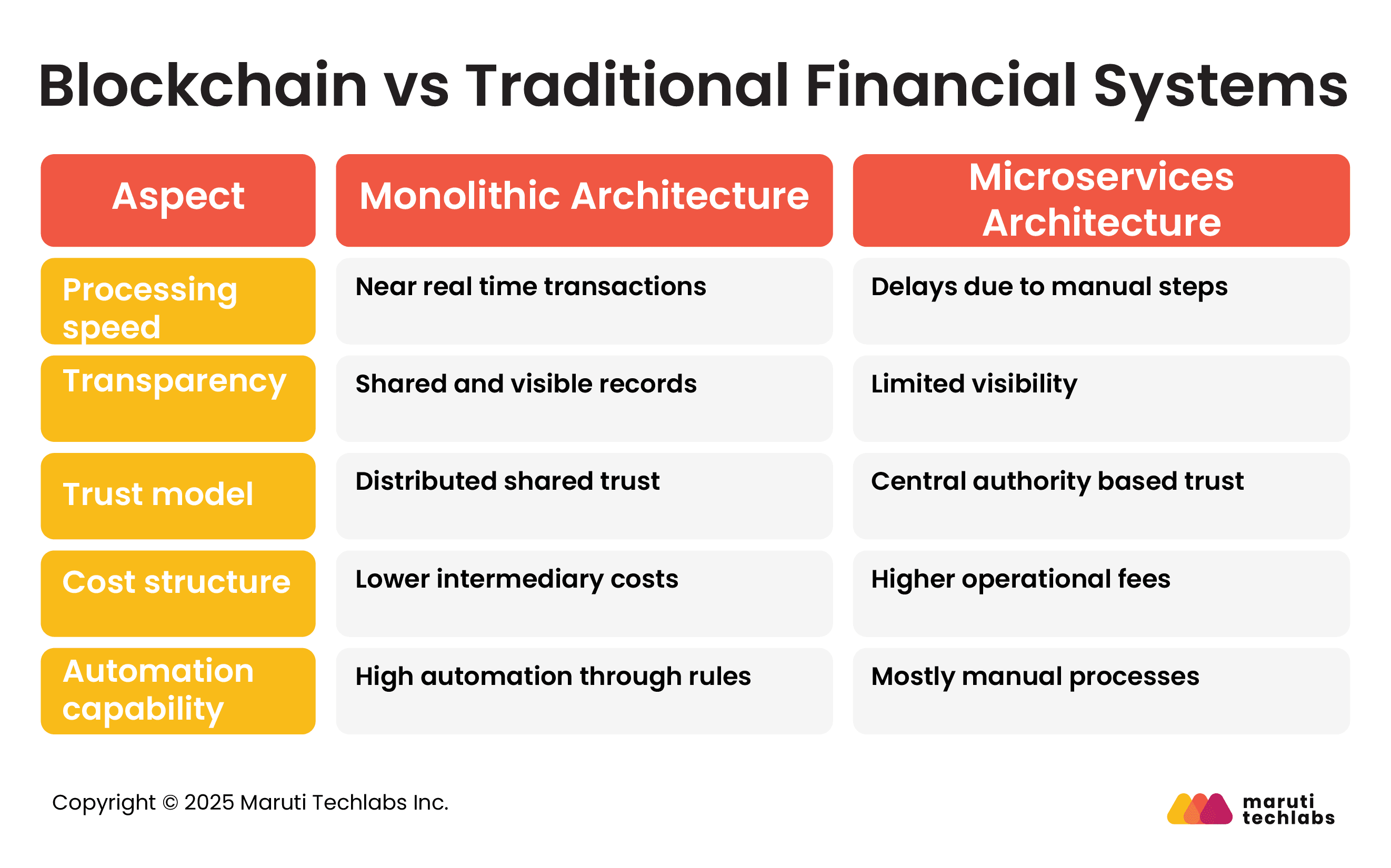
Here is a brief comparison between blockchain and conventional financial systems.
To benefit from blockchain, financial businesses must prepare strategically. This includes building skills, updating platforms, planning compliance, selecting partners carefully, and managing risks to ensure successful and sustainable adoption.
Organizations should invest in training teams on blockchain fundamentals and practical use cases. Building internal knowledge supports better decision-making and implementation.
Skilled teams help reduce reliance on external vendors and enable financial businesses to innovate confidently with emerging technologies.
Financial platforms should assess current systems for compatibility with blockchain integration. Modernizing infrastructure, improving data quality, and adopting flexible architectures help ensure smooth integration.
Platform readiness reduces disruption and supports scalable blockchain adoption aligned with long-term business goals
Early compliance planning is essential for blockchain adoption. Financial businesses must understand regulatory requirements and design systems that support auditability and reporting.
Proactive planning reduces legal risk and builds trust with regulators, customers, and partners from the beginning.
Choosing the right technology and implementation partners is critical. Financial businesses should evaluate partners based on experience, security practices, and regulatory understanding.
Strong partnerships reduce implementation risk and ensure blockchain solutions align with business objectives and compliance needs.
A thorough risk assessment helps identify technical, operational, and regulatory challenges. Financial businesses should evaluate potential impacts and define mitigation strategies.
Continuous risk monitoring ensures blockchain initiatives remain secure, compliant, and aligned with evolving business and market conditions.
The future of financial platforms will combine blockchain with intelligent technologies to improve decision-making, automation, and trust.
This integration will reshape how financial services are delivered, governed, and experienced by users.
Governments and regulators are developing clearer frameworks for blockchain use in finance. Future regulations will focus on consumer protection, transparency, and accountability.
More explicit rules will encourage broader adoption by reducing uncertainty and enabling financial platforms to invest confidently in compliant blockchain solutions.
Large financial institutions are increasingly adopting blockchain for payments, settlement, and asset management. As confidence grows, more institutions will move from pilots to full-scale deployment.
This shift will normalize blockchain use and accelerate its integration into mainstream financial services globally.
Web3 introduces user-controlled digital finance built on blockchain networks. Financial platforms will explore new models that prioritize ownership, transparency, and direct participation.
This evolution may redefine customer relationships, data control, and value exchange across digital financial ecosystems.
Enterprise-focused blockchain systems are designed for performance, privacy, and regulatory compliance. Financial platforms will increasingly adopt these systems to support complex operations.
Such solutions offer controlled access, scalability, and integration capabilities suited for large-scale financial environments.
Blockchain is used in finance as a secure digital ledger to record and verify transactions without intermediaries. It helps banks send cross-border payments faster and with lower fees. Financial markets use it to settle trades in near-real time, rather than waiting several days. Smart contracts automate loans, insurance claims, and compliance processes. Overall, blockchain improves transparency, reduces fraud, and cuts operational costs in financial services.
Finance technologies are moving toward smarter, faster, and more personalized digital services. AI and automation will handle lending, fraud detection, and customer support with minimal human effort. Blockchain and digital currencies will make payments instant and transparent across borders. Cloud platforms will reduce costs while improving security and scalability. Overall, the future of finance will be fully connected, data-driven, and customer-first, creating more clicks and engagement online.
Blockchain-based payment processing enables businesses and banks to transfer money through a decentralized, encrypted ledger rather than traditional gateways. It reduces transaction time from days to minutes, especially for cross-border payments. The technology cuts processing fees by removing multiple intermediaries and reconciliation steps. Every payment is time-stamped and traceable, improving transparency and preventing fraud. Overall, blockchain makes digital payments faster, more secure, and more reliable for modern financial systems.


